|
B
Top |
|
Bimodal distribution:
A distribution that has two modes. |
|
Box-and-whisker plot:
A plot that shows the center, spread, and skewness of a data
set by drawing a box and two whiskers using the median, the
first quartile, the third quartile, and the smallest and the
largest values in the data set between the lower and the
upper inner fences.
|
|
C
Top |
|
Census: A survey that includes all members of the
population. |
|
Continuous variable:
A (quantitative) variable that can assume any numerical
value over a certain interval or intervals. |
|
Coefficient of variation:
A measure of relative variability that expresses standard
deviation as a percentage of the mean. |
|
Coefficient of determination:
A measure that gives the proportion (or percentage) of the
total variation in a dependent variable that is explained by
a given independent variable.
|
|
D
Top |
|
Data or data set:
Collection of observations or measurements on a variable.
|
|
Descriptive statistics:
Collection of methods that are used for organizing,
displaying, and describing data using tables, graphs, and
summary measures.
|
|
Discrete variable:
A (quantitative) variable whose values are countable. |
|
Degrees of freedom for a simple linear regression
model:
Sample size minus 2, that is, n -2. |
|
Dependent variable:
The variable to be predicted or explained. |
Deterministic model:
A model in which the independent variable determines the
dependent variable exactly. Such a model gives an exact
relationship between two variables.
|
|
E
Top |
|
Element or member:
A specific subject or object included in a sample or
population. |
|
Empirical rule: For a specific bell-shaped distribution,
about 68% of the observations fall in the interval
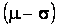 to to
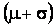 , about 95% fall in the interval , about 95% fall in the interval
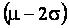 to to
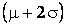 , and about 99.7% fall in the interval , and about 99.7% fall in the interval
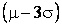 to to
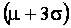 . . |
Estimated or predicted value of
y: The value of the dependent variable,
denoted by
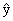 , that is calculated for a given value of x using the
estimated regression model. , that is calculated for a given value of x using the
estimated regression model.
|
|
F
Top |
|
·
First quartile:
The value in a ranked data set such that
about 25% of the measurements are smaller than this value
and about 75% are larger. It is the median of the values
that are smaller than the median of the whole data set.
|
|
I
Top |
|
Inferential statistics:
Collection of methods that help make decisions about a
population based on sample results. |
|
Interval scale: Data that can be ranked and for which we
can find the difference between two values are said to have
an interval scale. |
|
Inter quartile range:
The difference between the third and the first quartiles.
|
Independent or explanatory variable:
The variable included in a model to explain the variation in
the dependent variable.
|
|
L
Top |
|
Least squares estimates of A and B:
The values of a and b that are calculated by
using the sample data. |
|
Least squares method:
The method used to fit a regression line through a scatter
diagram such that the error sum of squares is minimum.
|
|
Least squares regression line:
A regression line obtained by using the least squares
method. |
|
Linear correlation coefficient:
A measure of the strength of the linear relationship between
two variables. |
Linear regression model:
A regression model that gives a straight line relationship
between two variables.
|
|
M
Top |
|
Multiple regression model:
A regression model that contains two or more independent
variables. |
|
Measures of dispersion:
Measures that give the spread of a distribution. The range,
variance, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation
are four such measures. |
|
Measures of position:
Measures that determine the position of a single value in
relation to other values in a data set. Quartiles,
percentiles, and percentile rank are examples of measures of
position. |
|
Median: The value of the middle term in a ranked data
set. The median divides a ranked data set into two equal
parts.
|
|
Mode: A value (or values) that occurs with highest
frequency in a data set. |
|
Multimodal distribution:
A distribution that has more than two modes. Bimodal is a
special case of a multimodal distribution with two modes.
|
|
Mean A measure of central tendency:
calculated by dividing the sum of all values by the number
of values in the data set. |
|
Measures of central tendency:
Measures that describe the center of a distribution. The
mean, median, and mode are three of the measures of central
tendency.
|
|
N
Top |
|
Negative relationship between two variables:
The value of the slope in the regression line and the
correlation coefficient between two variables are both
negative. |
|
Nominal scale: Data that are divided into different
categories that are used for identification purposes only
are said to have a nominal scale. |
|
Nonlinear (simple) regression model:
A regression model that does not give a straight line
relationship between two variables.
|
|
O
Top |
|
Outliers or extreme values:
Values those are very small or very large relative to the
majority of the values in a data set. |
|
Observation or measurement:
The value of a variable for an element. |
|
Ordinal scale: Data that can be divided into different
categories that can be ranked are said to have an ordinal
scale.
|
|
P
Top |
|
Parameter: A summary measure calculated for population
data. |
|
Percentile rank: The percentile rank of a value gives the
percentage of values in the data set that are smaller than
this value. |
|
Percentiles: Ninety-nine values that divide a ranked
data set into 100 equal parts. |
|
Population or target population:
The collection of all elements whose characteristics are
being studied. |
|
Population parameters for a simple regression
model:
The values of A and B for the regression model
y = A + bx +
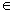 that are obtained by using population data. that are obtained by using population data. |
|
Positive relationship between two variables:
The value of the slope in the regression line and the
correlation coefficient between two variables are both
positive.
|
|
Prediction interval:
The confidence interval for a particular value of y
for a given value of x. Probabilistic or statistical
model A model in which the independent variable does not
determine the dependent variable exactly.
|
|
Q
Top |
|
Quartiles: Three summary measures that divide a ranked data
set into four equal parts. |
|
Qualitative or categorical data:
Data generated by a qualitative variable. |
|
Qualitative or categorical variable:
A variable that cannot assume numerical values but is
classified into two or more categories. |
|
Quantitative data:
Data generated by a quantitative variable.
|
|
Quantitative variable:
A variable that can be measured numerically.
|
|
R
Top |
|
Range: A measure of spread obtained by taking
the difference between the largest and the smallest values
in a data set. |
|
Random sample: A sample drawn in such a way that each
element of the population has some chance of being included
in the sample. |
|
Ratio scale: Data that can be ranked and for which all
arithmetic operations can be performed are said to have a
ratio scale. |
|
Representative sample:
A sample that contains the characteristics of the
corresponding population. |
|
Random error term (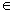 ): The difference between the actual and predicted values of y. ): The difference between the actual and predicted values of y.
|
|
S
Top |
|
Scatter diagram or scatter gram:
A plot of the paired observations of x and y. |
|
Simple linear regression:
A regression model with one dependent and one independent
variable that assumes a straight line relationship. |
|
Slope: The coefficient of x in a regression
model that gives the change in y for a change of one unit in
x. |
|
SSE: (error sum of squares) The sum of the squared
differences between the actual and predicted values of y.
It is that portion of the SST that is not explained by
the regression model. |
|
SSR (regression sum of squares): That portion of the
SST that is explained by the regression model. |
|
SST (total sum of squares): The sum of the squared
differences between actual y values and y. |
|
Standard deviation of errors:
A measure of spread for the random errors. |
|
Second quartile: Middle or second of the three quartiles
that divide a ranked data set into four equal parts. About
50% of the values in the data set are smaller and about 50%
are larger than the second quartile. The second quartile is
the same as the median. |
|
Sample: A portion of the population of interest.
|
|
Sample survey: A survey that includes elements of a
sample.
|
|
Statistics: Collection of methods that are used to collect,
analyze, present, and interpret data and to make decisions.
|
|
Survey: Collecting data on the elements of a
population or sample. |
|
Standard deviation:
A measure of spread that is given by the positive square
root of the variance. |
|
Statistic: A summary measure calculated for sample data.
|
|
T
Top |
|
Third quartile: Third of the three quartiles that divide
a ranked data set into four equal parts. About 75% of the
values in a data set are smaller than the value of the third
quartile and about 25% are larger. It is the median of the
values that are greater than the median of the whole data
set.
|
|
U
Top |
|
Unimodal distribution:
A distribution that has only one mode.
|
|
V
Top |
|
Variable: A characteristic under study or investigation
that assumes different values for different elements. |
|
Variance: A measure of spread.
|
|
Y
Top |
|
Y-Intercept: The point at which the regression line
intersects the vertical axis on which the dependent variable
is marked. It is the value of y when x is
zero. |
|